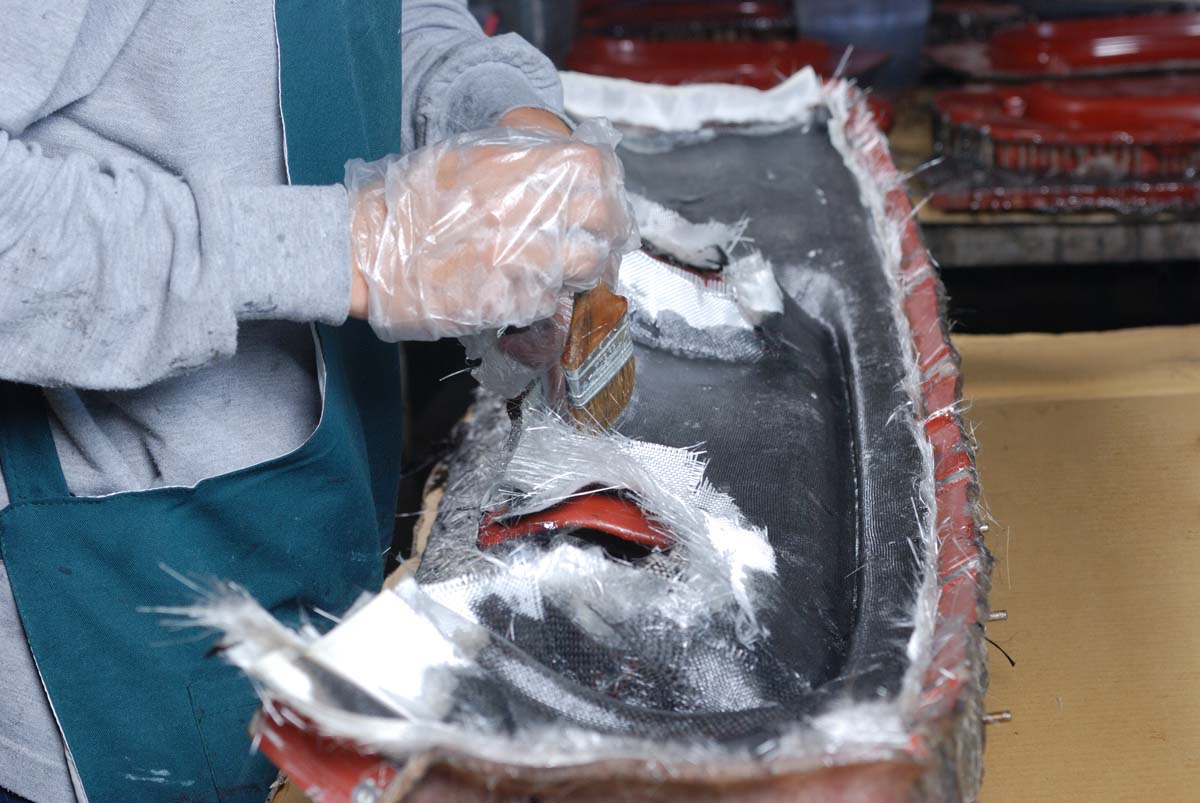
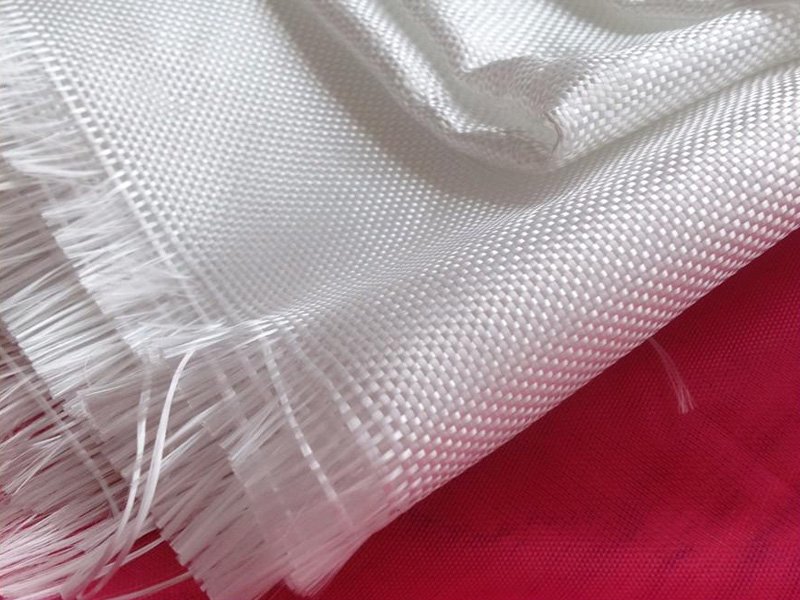
Glass fiber can pose significant risks to the human body when exposed for extended periods to environments containing it. Prolonged exposure can result in various health conditions, including eye damage, skin irritation, and respiratory issues.
Eye damage: Long-term exposure to glass fiber environments can lead to cornea and conjunctiva inflammation, causing symptoms like eye pain, photophobia, tearing, and other irritations. In severe cases, it may even result in vision loss.
Skin damage: Individuals exposed to glass fiber over extended periods may experience skin irritation, leading to roughness and redness. Inflammation can occur, leading to conditions like contact dermatitis, characterized by skin rashes and blisters.
Respiratory damage: Workers who inhale glass fiber fibers over time may suffer from throat irritation, itchiness, and coughing. Prolonged accumulation of glass fibers in the lungs can impair lung function and lead to pneumoconiosis. For those allergic to glass fiber, inhalation may trigger allergic asthma.
Continuous Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites (CFRT) are composite materials made of glass fiber as reinforcement and thermoplastic resin as the matrix through a melt impregnation process. During this process, glass fiber filaments are encapsulated within the prepreg, reducing exposure and potential harm to fabricators, constructors, recyclers, and individuals exposed to the material long-term. These composites serve as reinforced surface materials for plastic honeycomb panels.

CFRT full name is Continuous Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites. It is a composite material made of glass fiber as reinforcement material and thermoplastic resin as matrix by melt impregnation process.
By this process, the glass fiber filaments are laminated into the prepreg and the fibers are not exposed, which reduces the exposure of the glass fiber filaments to fabricators, constructors and post-process recyclers, or any body damage in the long-term exposure to the glass fiber environment. As a reinforced composite surface material for plastic honeycomb panels.
Fiber reinforced thermoplastics offer several advantages:
1. Better toughness compared to traditional plastics.
2. No chemical reactions during processing, resulting in shorter molding cycles.
3. Prepreg materials do not require specific storage conditions, making them easy to use.
4. Wide temperature range usability and low water absorption rate.
5. Simplified part molding process, leading to reduced manufacturing costs.
6. Facilitates waste recycling, emission reduction, and environmental protection.
Through plastic modification and the addition of fibrous substances for reinforcement, common plastics can exhibit enhanced performance in several aspects:
1. Improved mechanical strength, including tensile, bending, compression, modulus of elasticity, and creep resistance.
2. Increased heat deflection temperature.
3. Reduced coefficient of linear expansion.
4. Lower water absorption and increased dimensional stability.
5. Enhanced hardness.
6. Inhibition of stress cracking.

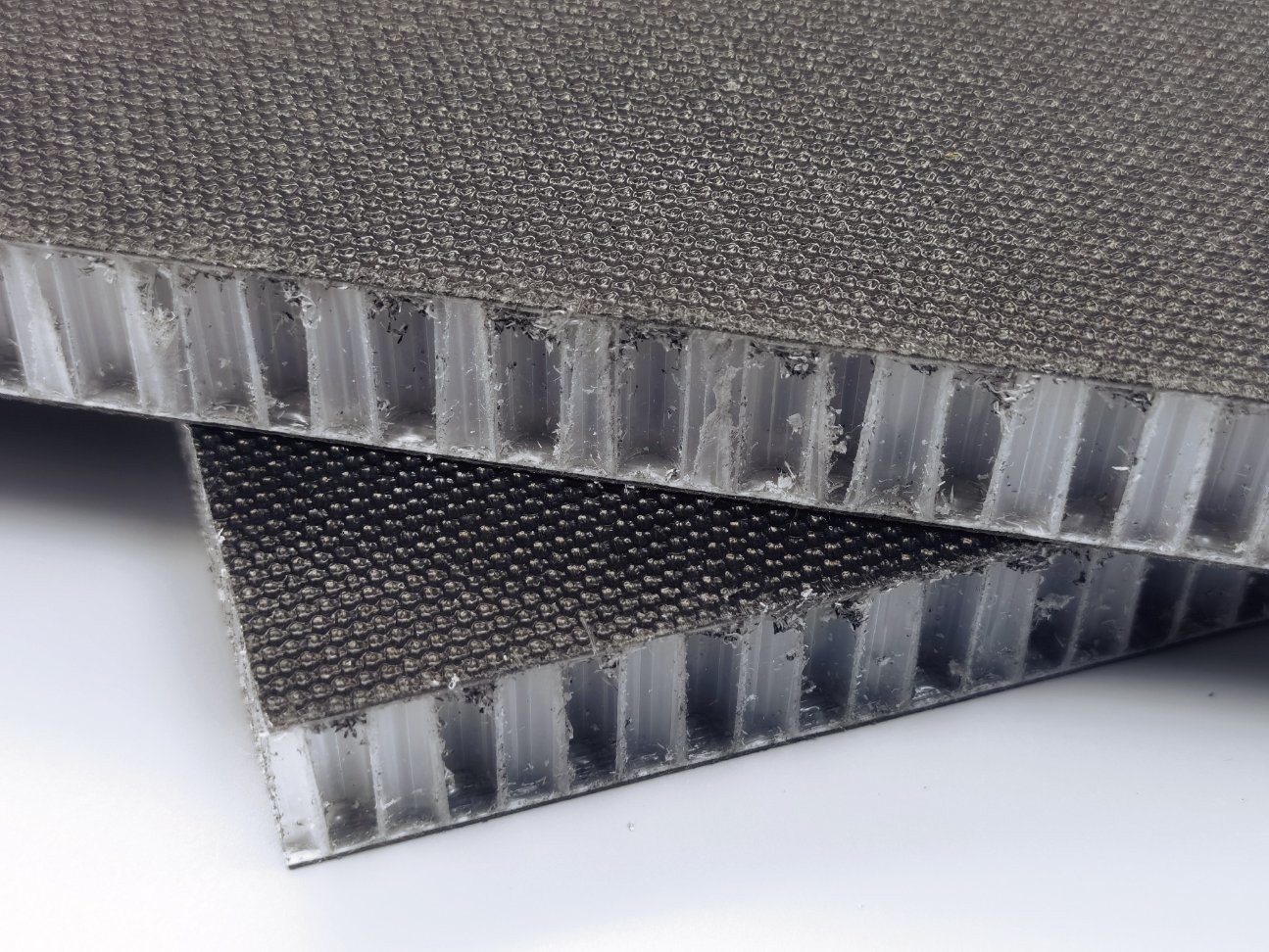


CFRT PP honeycomb composite panels is a creative combination of skin material and honeycomb core that makes thermoplastic composite panels lighter and stronger
Higher strength: The surface of the FRP, has good scratch resistance, impact resistance and corrosion resistance, excellent impact resistance and shear performance. The thermoplastic sheets are laminated at different angles to strengthen the skin. It is a wonderful structure that provides a much higher strength-to-weight ratio than conventional materials
Lighter weight: The honeycomb itself adopts the honeycomb nest structure, which uses less material and is light in weight. CFRT is based on the basis of ensuring high strength and high hardness, more lightweight
Stronger toughness: CFRT is to add horizontal or vertical and horizontal glass fibers to the resin, its toughness.
Easy to process and assemble: when the adhesive is cured with the glass fiber bond, it can be sawed, drilled, punched and cut into shape, and has a wide range of applications in the shipbuilding industry. Glass fiber is mainly used for thermal and acoustic insulation, to create waterproof surfaces, and as a reinforcing agent for plastics and other composites.

